Dementia and other cognitive disorders are conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. These disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s life, as well as their loved ones. Understanding what these disorders are and how they affect a person can help increase awareness and promote early diagnosis and treatment.
What is Dementia?
Dementia is not a single disease, but rather a term used to describe a range of symptoms associated with a decline in memory, thinking, and communication skills. It is a progressive condition that worsens over time and can significantly interfere with an individual’s daily activities and independence. The most common cause of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, accounting for 60-80% of cases. Other types of dementia include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and mixed dementia.
What are the Symptoms of Dementia?
The symptoms of dementia can vary depending on the type and stage of the condition. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
1. Memory loss: This is the most well-known symptom of dementia. People may experience difficulty remembering recent events, names, or conversations.
2. Difficulty with everyday tasks: As dementia progresses, individuals may have trouble performing routine tasks such as cooking, cleaning, or getting dressed.
3. Communication problems: Dementia can make it challenging to express thoughts and feelings, or follow conversations.
4. Confusion: People with dementia may become disoriented in familiar places or lose track of time.
5. Behavioral changes: Dementia can cause changes in mood, personality, and behavior. Individuals may become agitated, suspicious, or withdrawn.
If you or a loved one are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
What are Other Cognitive Disorders?
Apart from dementia, there are other cognitive disorders that can also impact a person’s ability to think, remember, and communicate. These include:
1. Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): MCI is a condition that affects memory and thinking skills but does not interfere with daily activities. It is a potential precursor to dementia, but not everyone with MCI will develop the condition.
2. Delirium: Delirium is a sudden change in mental status that can cause confusion, disorientation, and changes in behavior or emotions. It often occurs as a result of a medical condition, medication, or substance use and is reversible with proper treatment.
3. Huntington’s disease: This is a genetic disorder that causes the degeneration of brain cells, leading to cognitive, motor, and psychiatric symptoms.
4. Parkinson’s disease: While Parkinson’s disease is primarily known for its motor symptoms, it can also cause cognitive impairment in some individuals.
How are These Disorders Diagnosed?
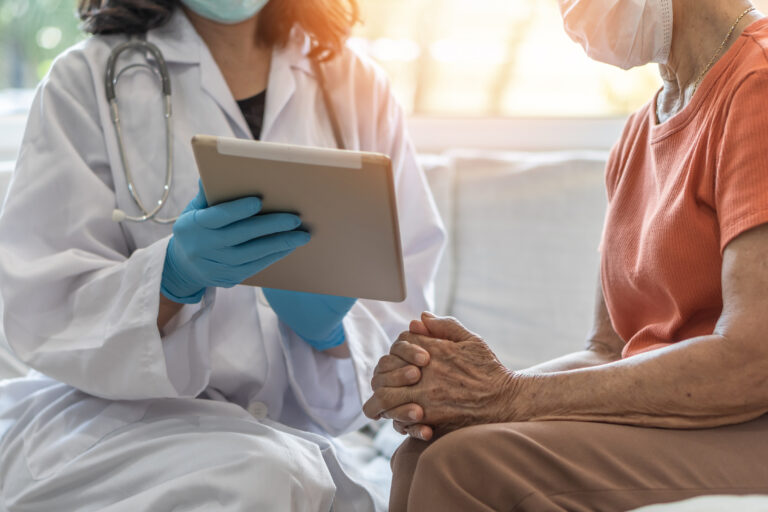
Diagnosing dementia and other cognitive disorders can be challenging, as many of the symptoms overlap with other conditions. A doctor will typically conduct a thorough physical and neurological exam, review medical history, and perform memory and cognitive tests to make an accurate diagnosis. They may also order imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to rule out other potential causes.
Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for most types of dementia and other cognitive disorders, there are treatment options available to manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the condition. These may include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
1. Medications: Depending on the type of dementia or cognitive disorder, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms such as memory loss, anxiety, or depression.
2. Therapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals cope with the emotional and behavioral changes caused by these disorders.
3. Lifestyle Changes: Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, eating a healthy diet, and staying physically active may help slow down the progression of cognitive decline.
Seeking Support
Caring for someone with dementia or another cognitive disorder can be emotionally and physically draining, and it is essential to seek support. Support groups, counseling, and respite care can provide caregivers with the resources and assistance they need.
In conclusion, dementia and other cognitive disorders are complex conditions that can significantly impact a person’s life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with these disorders. Remember to seek medical attention if you or a loved one are experiencing any concerning symptoms. And for those who are caring for someone with a cognitive disorder, do not hesitate to seek support. With proper care and support, individuals with these disorders can continue to live fulfilling lives.