Blunt force trauma, which refers to injury caused by impact with a non-sharp object, often results in a range of physical and psychological consequences that can significantly affect both the injured individual and their caregivers. The association between blunt force trauma and increased caregiver burden is a complex and multifaceted issue that involves medical, psychological, and social dimensions.
**Medical and Psychological Impact of Blunt Force Trauma**
Blunt force trauma can cause injuries ranging from mild bruises to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), fractures, internal organ damage, and long-term disabilities. Among these, traumatic brain injury is particularly relevant to caregiver burden because it often leads to cognitive, emotional, and behavioral impairments that require ongoing care and supervision. Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), commonly known as concussion, can also have lasting effects such as memory problems, mood disorders, and sleep disturbances, which complicate caregiving demands[4][5].
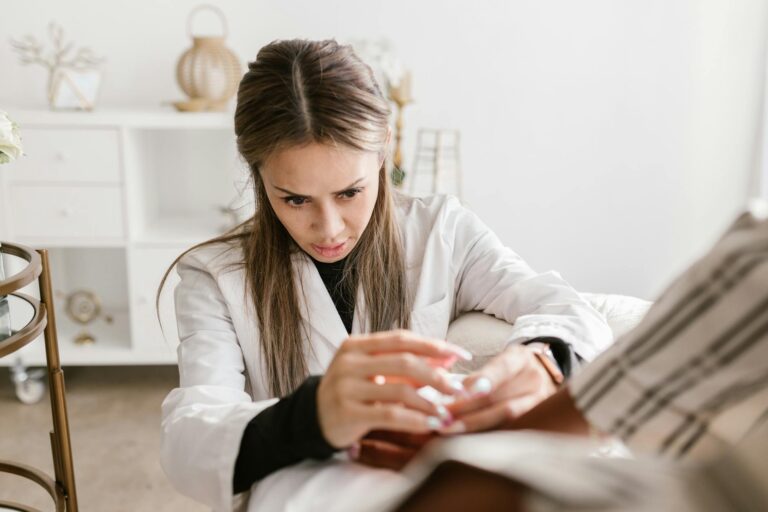
The psychological impact of trauma extends beyond the patient to their caregivers. Caregivers often experience emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and feelings of guilt or helplessness, especially when the trauma affects children or vulnerable adults[2]. The caregiving role may involve managing complex medical needs, behavioral changes, and rehabilitation processes, which can be physically and emotionally exhausting.
**Caregiver Burden Defined**
Caregiver burden refers to the physical, emotional, social, and financial strain experienced by individuals who provide care for someone with chronic illness, disability, or trauma-related impairments. This burden can manifest as stress, social isolation, reduced quality of life, and even health problems for the caregiver themselves[1][3].
**Linking Blunt Force Trauma to Increased Caregiver Burden**
1. **Severity and Type of Injury**
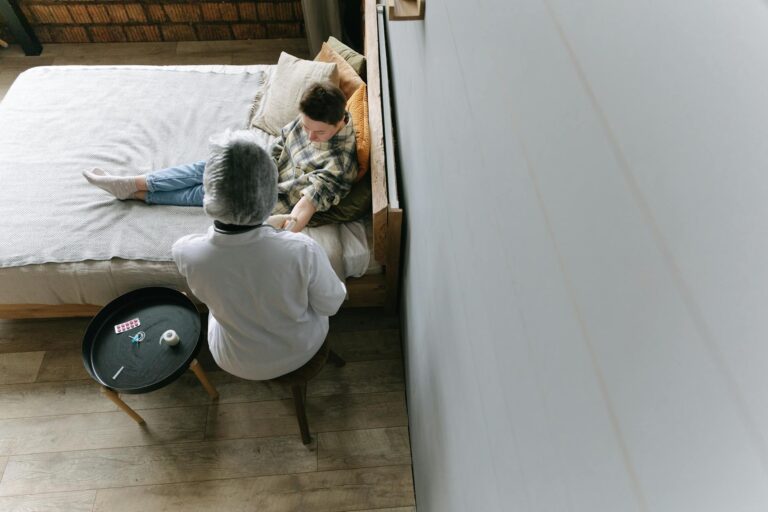
The severity of blunt force trauma directly influences caregiver burden. Severe injuries, such as those involving brain trauma or multiple fractures, often require intensive, long-term care. This includes assistance with daily living activities, medication management, and coordination of medical appointments, which increases caregiver workload and stress[4].
2. **Cognitive and Behavioral Changes**
Traumatic brain injuries resulting from blunt force trauma can cause cognitive deficits (e.g., memory loss, impaired judgment) and behavioral changes (e.g., irritability, aggression). These changes complicate caregiving because they require constant supervision and specialized behavioral management strategies, increasing emotional and physical demands on caregivers[4].
3. **Emotional and Psychological Effects on Caregivers**
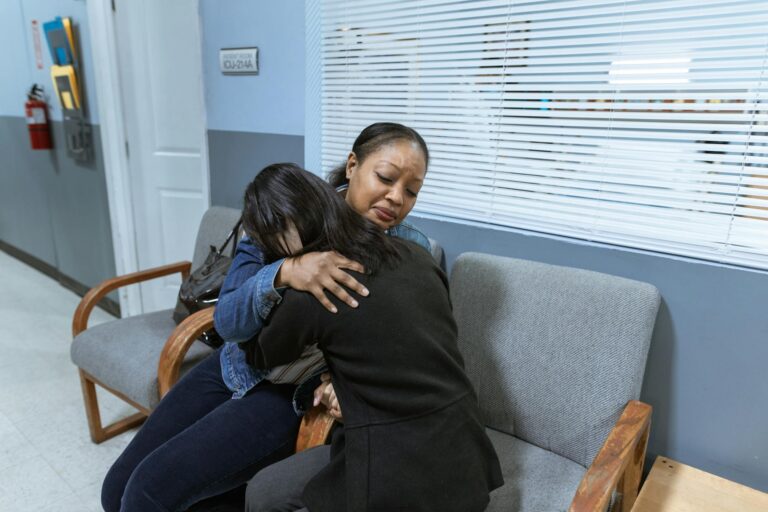
Caregivers of trauma survivors frequently report feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression. The trauma’s impact on family dynamics and interpersonal relationships can exacerbate these feelings, as caregivers may struggle with altered roles and expectations within the family unit[1][2].
4. **Impact on Children and Family Systems**
When blunt force trauma affects children, caregivers often face additional challenges. Research shows that childhood trauma not only affects the child but also induces distress, guilt, and anxiety in caregivers, which can heighten caregiver burden. Effective treatment models that include caregiver support have been shown to improve outcomes for both children and their caregivers[2].
5. **Social and Financial Strain**
The need for ongoing medical care, rehabilitation, and sometimes home modifications can impose significant financial burdens on families. Caregivers may reduce work hours or leave employment entirely to provide care, leading to economic hardship and increased stress[3].
6. **Sleep Disturbances and Health Decline in Caregivers**
Caregivers often experience disrupted sleep due to caregiving responsibilities, which can worsen their physical and mental health. Studies assessing sleep quality in caregivers of trauma survivors highlight the importance of addressing caregiver health to reduce overall burden[2].
**Interventions and Support**
Addressing caregiver burden associated with blunt force trauma requires a holistic approach:
– **Medical and Rehabilitation Support:** Comprehensive rehabilitation programs for trauma survivors, including cognitive and behavioral therapies, can reduce caregiving demands by improving patien