**How Chronic Loneliness Affects Your Brain**
Chronic loneliness is more than just a feeling of being alone. It can have serious effects on your brain and overall health. In this article, we will explore how chronic loneliness can impact your brain and why it’s crucial to address it.
### What is Chronic Loneliness?
Chronic loneliness is a long-term feeling of isolation and disconnection from others. It’s different from temporary loneliness, which might make you feel a bit down but eventually passes. Chronic loneliness can make you feel like you’re in your own world, even when you’re surrounded by people.
### How Does Chronic Loneliness Affect the Brain?
Research shows that chronic loneliness can change the way your brain works. Here are some key points:
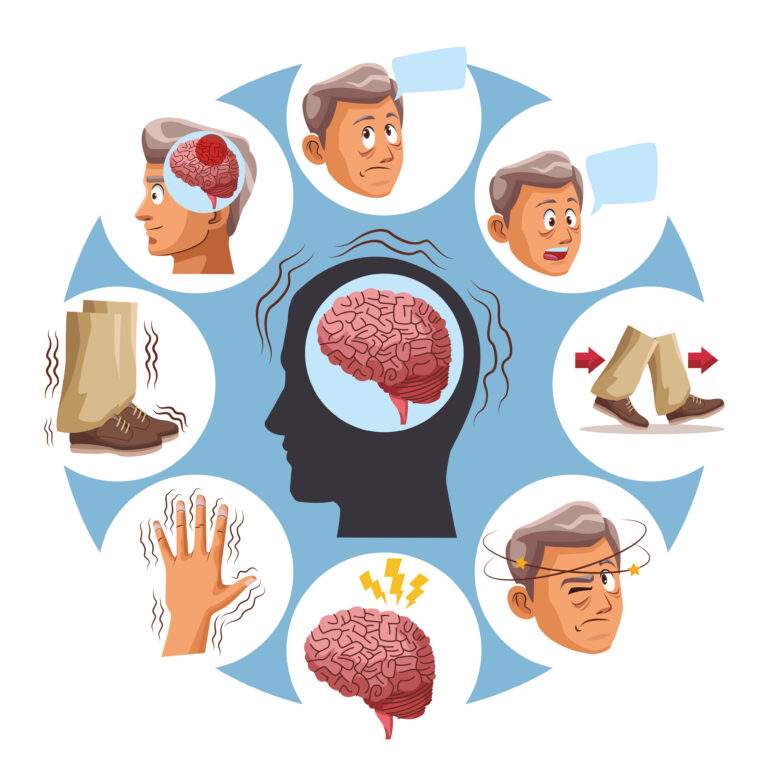
– **Increased Risk of Dementia**: Studies have found that people who experience chronic loneliness are more likely to develop dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. This is because social isolation can reduce neural activity and weaken connections in the brain that are essential for cognitive health[1][2][3].
– **Brain Structure Changes**: Chronic loneliness can alter the structure of the brain, particularly in areas related to social interaction and emotional regulation. This can lead to difficulties in concentrating, making decisions, and problem-solving[1][3].
– **Stress and Cortisol**: When you feel lonely, your body produces more cortisol, a hormone associated with stress. High levels of cortisol over time can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues[1][3].
### Physical Health Consequences
Chronic loneliness doesn’t just affect the brain; it also has significant physical health consequences. These include:
– **Heart Disease and Stroke**: Isolation can increase blood pressure and inflammation, which are risk factors for heart disease and stroke. People who feel lonely are more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors like poor diet and lack of exercise, further exacerbating cardiovascular risks[2][3].
– **Type 2 Diabetes**: Prolonged loneliness can lead to unhealthy habits such as overeating and sedentary lifestyles, contributing to the development of Type 2 diabetes[2].
### Mental Health Impact
Mental health is also severely impacted by chronic loneliness. It can lead to:
– **Depression and Anxiety**: Loneliness is a leading cause of depression and anxiety. People who live alone or feel socially disconnected often experience feelings of worthlessness and sadness, which can spiral into clinical depression[2][4].
– **Suicidal Thoughts**: Chronic loneliness can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts. The feeling of being disconnected from others can make people feel like they are a burden to those around them, leading to intense self-hatred and despair[4].
### Combating Chronic Loneliness
Addressing chronic loneliness is crucial for both mental and physical health. Here are some steps you can take:
– **Seek Social Interaction**: Engage in group activities, join clubs or organizations, or volunteer. These activities can help you connect with others and build meaningful relationships[1].
– **Therapy and Support**: Consider therapy or counseling to address underlying issues that might be contributing to your loneliness. Support groups can also provide a sense of community and connection[1][3].
– **Stay Active**: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve mood. It’s also a great way to meet new people and build social connections[2].
In conclusion, chronic loneliness is not just a feeling; it’s a serious condition that can affect your brain and overall health. By understanding its effects and taking steps to address it, you can improve your mental and physical well-being. Remember, you are not alone, and there are many resources available to help you combat chronic loneliness.