Dementia is a condition that affects the brain and can make it hard for people to remember things, think clearly, and do everyday tasks. One of the most common signs of dementia is forgetting how to do simple things that used to be easy, like making a cup of tea, remembering to turn off the stove, or even finding the right words during a conversation. These problems happen because dementia changes the way the brain works, making it harder to store and recall information, and sometimes making it difficult to focus or pay attention to what is happening around them [2].
When someone has dementia, their memory and thinking skills start to decline. At first, this might mean they forget small details, like where they left their keys or what day it is. But as the condition progresses, they may start to forget how to do things that they have done many times before, such as cooking a meal, getting dressed, or managing their money. This is not just normal forgetfulness that everyone experiences from time to time. It is a more serious problem that can affect a person’s ability to live independently and take care of themselves [2].
One of the main reasons dementia makes people forget everyday tasks is because it affects the parts of the brain that are responsible for memory, attention, and problem-solving. For example, someone with dementia might have trouble remembering the steps needed to complete a task, like following a recipe or using a washing machine. They might also struggle to concentrate on what they are doing, which can make it hard to finish a task or do it correctly. Sometimes, they may start a task but forget what they were doing halfway through, or they might do things in the wrong order [2].
Dementia can also make it difficult for people to recognize objects or understand how to use them. For instance, someone might forget what a spoon is for or how to use a remote control. This can be confusing and frustrating for both the person with dementia and their family members. In some cases, people with dementia may even forget how to speak or understand language, which can make it hard to communicate their needs or ask for help [2].
There are different types of dementia, and each one can affect people in slightly different ways. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia, and it often starts with memory problems. People with Alzheimer’s may forget recent events, repeat questions, or have trouble remembering names and places. As the disease progresses, they may also have difficulty with more complex tasks, like planning a trip or managing their finances [2].
Another type of dementia is called dementia with Lewy bodies, which can cause movement problems as well as memory and thinking issues. People with this type of dementia might have trouble with balance, coordination, and muscle control, which can make it hard to do everyday activities like walking, dressing, or eating. They may also experience changes in their mood, behavior, and sleep patterns [2].
Frontotemporal dementia is another type that can affect a person’s personality, emotions, and language skills. People with this type of dementia might have trouble finding the right words, understanding what others are saying, or expressing themselves clearly. They may also show changes in their behavior, such as becoming more impulsive or losing interest in activities they used to enjoy [2].
It is important to note that not all forgetfulness is a sign of dementia. Everyone forgets things from time to time, especially as they get older. Normal forgetfulness might include occasionally misplacing items, forgetting someone’s name, or having trouble remembering a word. But if someone is forgetting how to do everyday tasks, repeating the same question over and over, or having trouble with things they used to do easily, it could be a sign of dementia and they should see a doctor [2].
Early detection of dementia is important because it can help people get the right treatment and support. Researchers have found that certain changes in speech can be an early sign of cognitive decline, even before memory problems become noticeable. For example, longer pauses in speech, especially during memory tests, can reveal cognitive decline in its earlier phases. This means that if someone is taking longer to remember something, even if they eventually do, it could be a sign of early mental changes associated with dementia [3].
Scientists have also discovered that the speed of a person’s natural speech can be a predictor of cognitive decline. People who speak more slowly or have more pauses in their speech may be at higher risk of developing dementia. This is because a general slowdown in cognitive processing, not just memory, lies at the heart of cognitive decline. Neuroimaging studies have shown that people with greater evidence of tau tangles in their brains, which are linked to Alzheimer’s disease, tend to have a slower speech rate and more pauses in their speech [4].
Exercise has been shown to help slow the progression of dementia and reduce the risk of developing the condition. Studies have found that older adults who maintain moderate levels of physical activity, such as walking, have a significantly lower chance of developing dementia over time. Just 20 minutes of activity twice a week can make a difference. Exercise is also linked to a slower buildup of tau protein in the brain, which is associated with cell damage and death in Alzheimer’s disease. Taking around 5,000 steps a day can slow cognitive decline in people with early signs of Alzheimer’s, and this effect plateaus at around 5,000 to 7,500 steps a day [1, 5].
Other factors that can affect the risk of dementia include age, education, and cognitive function. The risk of developing dementia increases with age, but higher levels of education and better cognitive function can lower the risk. Sex does not appear to have an effect on the risk of dementia [1].
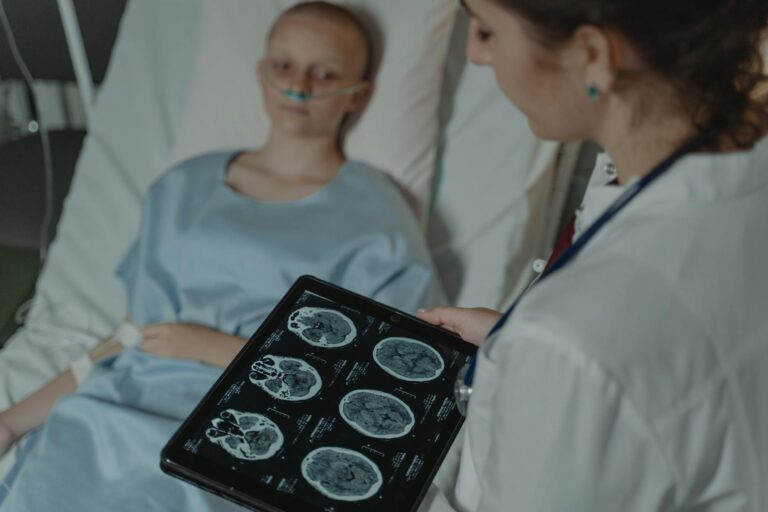
If someone is experiencing memory loss or other signs of dementia, it is important to seek medical advice. A doctor can perform tests to assess memory, thinking skills, and other cognitive functions. They may also use brain scans to look for signs of dementia, such as the buildup of beta-amyloid and tau proteins. Early diagnosis and treatment can help people manage their symptoms and maintain their independence for as long as possible [5].
In addition to medical treatment, there are things people can do to support brain health and reduce the risk of dementia. Staying physically active, eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and staying socially engaged can all help protect the brain. It is also important to manage other health conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and depression, which can increase the risk of dementia [1, 5].
Dementia can make it hard for people to remember everyday tasks, but with the right support and treatment, many people can continue to live fulfilling lives. Understanding the signs of dementia and seeking help early can make a big difference in managing the condition and maintaining quality of life.
[1] https://vitalrecord.tamu.edu/just-20-minutes-of-activity-twice-weekly-helps-halt-dementia/
[2] https://www.alzheimersresearchuk.org/news/spotting-early-signs-that-could-be-dementia-when-should-you-worry/
[3] https://www.lsu.edu/blog/2025/11/rb-dementia-ai.php
[4] https://www.sciencealert.com/scientists-discover-speech-trait