Dementia is a common disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It is a progressive neurological condition that impacts cognitive abilities such as memory, language, and decision-making. While there is currently no cure for dementia, there are ways to manage the condition and improve quality of life for individuals living with it. In recent years, brain games have emerged as a popular approach to improving memory and cognitive function in people with dementia. In this article, we will explore the science behind brain games and their potential benefits for individuals with dementia.

What are brain games?
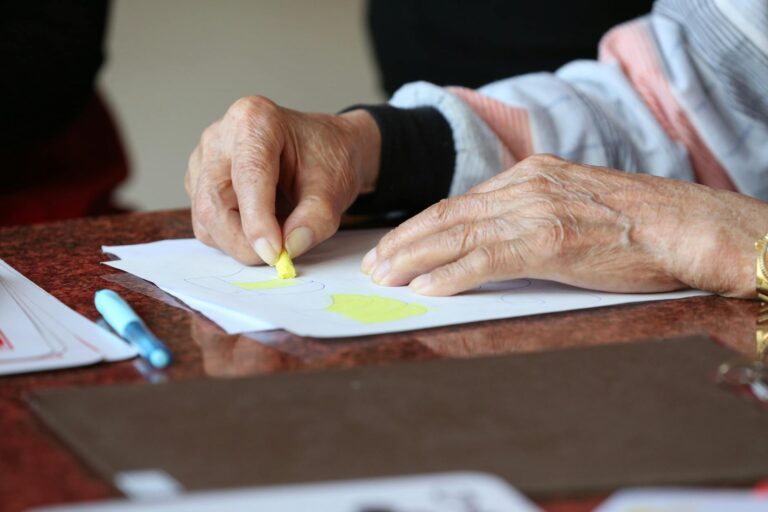
Brain games are games and activities that are designed to stimulate cognitive function and improve memory. They can take many different forms, from puzzles and crosswords to online games and apps. Brain games are typically designed to challenge the brain and encourage the formation of new neural pathways. They may also help to improve concentration, attention, and problem-solving skills.
The science behind brain games
The idea behind brain games is that by stimulating the brain through mental exercises, we can strengthen its neural connections and improve cognitive function. This is known as neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to new experiences. Studies have shown that regular mental exercise can lead to improvements in memory and cognitive function, as well as increased brain volume and connectivity.
The benefits of brain games for individuals with dementia
While brain games may be helpful for improving memory and cognitive function in healthy individuals, they may have even greater potential benefits for individuals with dementia. People with dementia often experience a decline in cognitive function and memory, which can impact their ability to perform daily activities and maintain their independence. Brain games may be able to slow down this decline and help individuals with dementia maintain their cognitive abilities for longer.
Several studies have investigated the effects of brain games on individuals with dementia. One study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found that playing computer games that focus on memory and problem-solving skills led to significant improvements in cognitive function and quality of life in individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Another study published in the Journal of Gerontology found that playing brain games was associated with a reduced risk of developing dementia in older adults.
It is important to note that while brain games may have some benefits for individuals with dementia, they are not a cure for the condition. Dementia is a complex disorder that requires a comprehensive treatment plan, which may include medication, lifestyle changes, and support from caregivers.
Choosing the right brain games
If you are interested in trying brain games to improve your memory or cognitive function, it is important to choose the right games. Look for games that are specifically designed to improve memory and cognitive function, and avoid games that are purely for entertainment. Some popular brain games that are designed for cognitive training include Lumosity, BrainHQ, and Elevate.
It is also important to remember that brain games are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to maintaining brain health. Other lifestyle factors, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, social engagement, and management of underlying medical conditions, are also important for maintaining brain health and reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
Conclusion
Brain games have emerged as a popular approach to improving memory and cognitive function in individuals with dementia. While the science behind brain games is still developing, there is evidence to suggest that they may have some benefits for individuals with mild cognitive impairment and early-stage dementia. If you are interested in trying brain games to improve your memory or cognitive function, be sure to choose games that are specifically designed for cognitive training and remember that they are just one piece of a comprehensive treatment plan for dementia. As always, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your treatment plan.