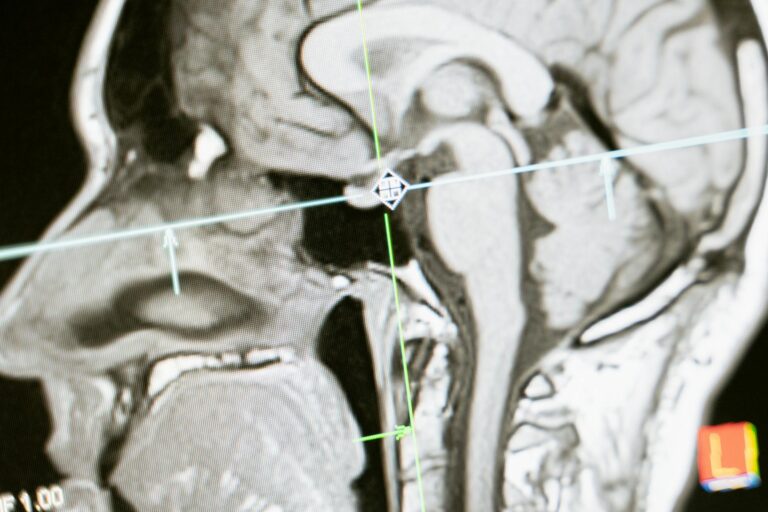
A stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood flow to a certain part of the brain is interrupted or reduced. This leads to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, causing brain cells to die. When this happens in the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) of the brain, it is known as a left MCA stroke. This type of stroke can have a significant impact on a person’s cognitive abilities, affecting their thinking, memory, and communication skills.
To understand the effects of a left MCA stroke on cognitive functions, we must first understand the role of the left MCA in the brain. The left MCA supplies blood to the left side of the brain, which is responsible for language, logical thinking, and analytical skills. Therefore, any damage to this area can result in various cognitive deficits.
One of the most common cognitive deficits associated with a left MCA stroke is aphasia, which is a language disorder. Depending on the severity of the stroke, a person may experience difficulty speaking, understanding speech, reading, and writing. This impairment can be a significant hurdle in everyday life, affecting social interactions, work, and daily activities. It can also lead to frustration and isolation for both the individual and their loved ones.
Besides aphasia, a left MCA stroke can also cause deficits in executive functions. These are a set of mental skills that help us plan, organize, and carry out tasks effectively. A stroke survivor may struggle with problem-solving, decision-making, and multitasking. They may also have difficulty with abstract thinking and planning ahead. These impairments can make it challenging for them to manage daily activities and tasks that require multiple steps.
Another cognitive deficit associated with a left MCA stroke is memory loss. This can manifest in different ways, ranging from mild forgetfulness to severe amnesia. Stroke survivors may have trouble remembering new information, such as names or appointments, and may also struggle with their long-term memory. This can affect their ability to learn new skills or retain new information.
Besides the above-mentioned deficits, a left MCA stroke can also cause changes in behavior and emotional regulation. This may include difficulty controlling emotions, such as anger, frustration, and depression. The stroke survivor may also have difficulty understanding other people’s emotions and may struggle with empathy. These changes in behavior can be challenging for both the individual and their loved ones to cope with.
It is worth noting that the severity and type of cognitive deficit vary from person to person, depending on the location and extent of the stroke. Some individuals may experience only mild impairments, while others may have more severe and extensive deficits. It is also possible for stroke survivors to experience a combination of different cognitive deficits.
While the effects of a left MCA stroke on cognitive functions can be overwhelming, there is hope for recovery. The brain has a remarkable ability to adapt and rewire itself, known as neuroplasticity. With the right treatment and rehabilitation, stroke survivors can improve their cognitive abilities and regain some of their lost functions.
Rehabilitation for cognitive deficits after a left MCA stroke typically involves a combination of therapies, including speech therapy, occupational therapy, and cognitive therapy. Speech therapy can help improve communication skills and language abilities, while occupational therapy can assist with daily activities and tasks. Cognitive therapy focuses on improving cognitive skills such as memory, attention, and problem-solving.
In addition to therapy, stroke survivors may benefit from making lifestyle changes to support brain health. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle changes can also help reduce the risk of future strokes.
In conclusion, a left MCA stroke can have significant cognitive effects on an individual, affecting their language, executive functions, memory, and behavior. The road to recovery may be challenging and require significant effort, but with the right treatment and support, stroke survivors can improve their cognitive abilities and achieve a better quality of life. It is essential for stroke survivors and their loved ones to remain patient, optimistic, and seek professional help to navigate through this journey of recovery.