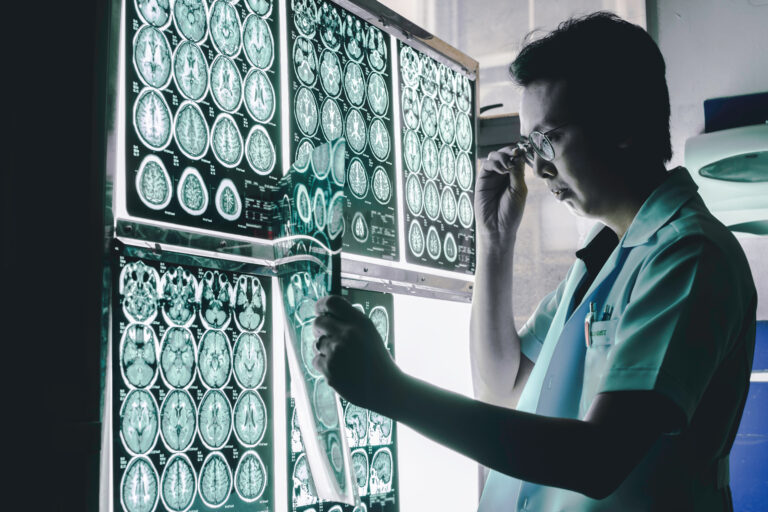
A CT scan can identify a stroke in dementia patients very quickly, often within minutes to an hour after the patient arrives at the hospital. This rapid detection is crucial because stroke is a medical emergency where every minute counts to reduce brain damage and improve outcomes. CT scans are widely used as the first imaging tool in suspected stroke cases because they are fast, accessible, and effective at detecting bleeding or large vessel blockages that cause strokes.
When a dementia patient experiences sudden neurological symptoms suggestive of a stroke, such as weakness, speech difficulties, or confusion, a CT scan is typically performed immediately. The scan can reveal whether the stroke is ischemic (caused by a blood clot blocking a vessel) or hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding in the brain). This distinction is vital because treatment approaches differ significantly. For example, clot-busting drugs are used for ischemic strokes but are dangerous if bleeding is present.
In dementia patients, the challenge is that their baseline brain changes—such as atrophy or small vessel disease—can complicate interpretation. However, modern CT technology combined with advanced analysis tools, including AI-driven methods, can help differentiate acute stroke lesions from chronic changes related to dementia. These tools can quantify brain atrophy and detect acute abnormalities quickly, supporting clinicians in making timely decisions.
The speed of CT scan identification depends on several factors:
– **Hospital protocols and availability:** Many stroke centers have protocols to perform CT scans within 20-30 minutes of patient arrival.
– **Patient condition and cooperation:** Dementia patients may have difficulty communicating symptoms, but emergency teams are trained to recognize stroke signs even in cognitively impaired individuals.
– **Imaging technology:** Modern CT scanners provide high-resolution images rapidly, often within seconds of scanning.
– **Expertise and AI assistance:** Radiologists and neurologists interpret scans quickly, and AI tools can provide automated assessments to highlight areas of concern.
Once the CT scan is done, the results are usually available immediately, allowing for urgent treatment decisions. This rapid turnaround is essential because treatments like thrombolysis or thrombectomy are time-sensitive and most effective when administered early.
In summary, a CT scan can identify a stroke in dementia patients very rapidly, often within minutes to an hour after hospital arrival, enabling prompt diagnosis and treatment. Despite the complexities dementia adds to brain imaging, advances in CT technology and analysis tools help ensure accurate and swift stroke detection in this vulnerable population.