The connection between gut health and aging is more intricate than you might think. Our gut microbiome, which is made up of trillions of microorganisms, plays a crucial role in how we age. As we get older, changes in our lifestyle, diet, and physical activity can affect the balance of these microbes, leading to a less diverse gut microbiome. This shift can have significant implications for our health, contributing to conditions like poor digestion, increased inflammation, and even chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
One of the most fascinating aspects of gut health is its link to longevity. People who live exceptionally long lives, like centenarians from Okinawa and Sardinia, have unique gut microbiomes characterized by high diversity and specific beneficial bacteria. These microbes help maintain a strong gut barrier, reduce inflammation, and support metabolic health, all of which are factors that contribute to a longer and healthier life.
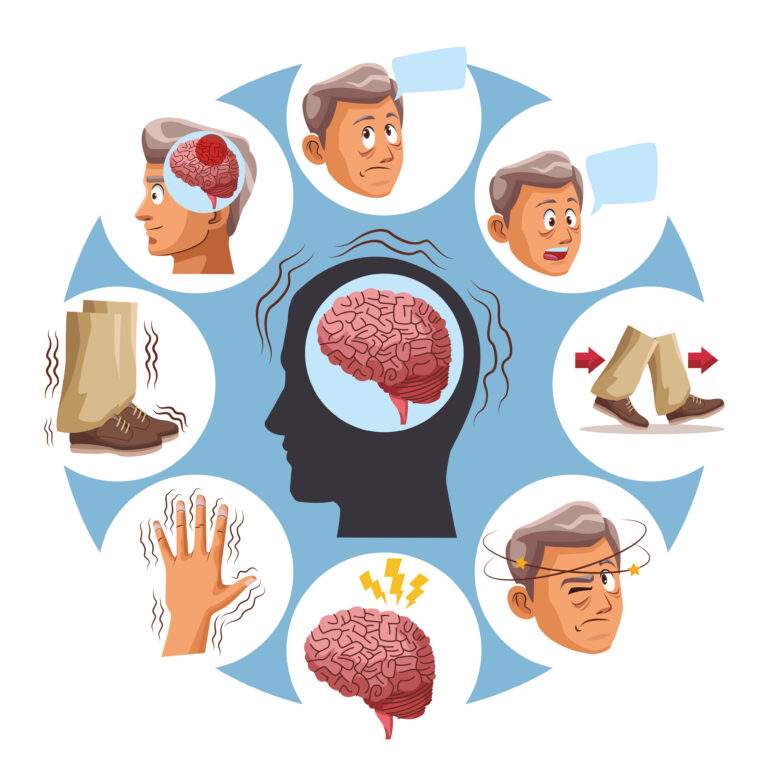
The gut and brain are also closely connected through what is known as the gut-brain axis. This means that changes in the gut microbiome can influence not just our physical health but also our mental well-being. Conditions like Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia have been linked to changes in the microbiome, highlighting the importance of maintaining good gut health for both body and mind.
As we age, our dietary habits often change, and we may consume less fiber, drink less water, and avoid certain foods that are beneficial for our gut. Additionally, medications and reduced physical activity can further disrupt the balance of our microbiome. Habits like excessive alcohol intake, lack of sleep, and chronic stress can also take a toll on gut health, causing it to age prematurely.
Fortunately, there are ways to support our gut microbiome as we age. Eating a varied diet rich in whole, plant-based foods can help maintain a diverse microbiome. Probiotics, which contain beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, have been studied for their potential benefits in aging and longevity. By understanding and addressing these factors, we can take steps to promote healthier aging and potentially extend our healthspan.