The Science Behind Amyloid Plaques and Tau Tangles
Alzheimer’s disease is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. At its core, it involves two main components: amyloid plaques and tau tangles. Understanding these elements is crucial for developing effective treatments and improving our knowledge of the disease.
### What Are Amyloid Plaques?
Amyloid plaques are deposits of a protein called beta-amyloid that accumulate in the brain. These proteins are naturally present in the body, but in Alzheimer’s disease, they start to clump together in a way that is harmful to brain cells. Over time, these clumps form large deposits known as plaques. The buildup of amyloid plaques disrupts communication between brain cells and can lead to cell death.
### What Are Tau Tangles?
Tau tangles are another type of protein deposit found in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease. Normally, tau proteins help stabilize the structure of brain cells. However, in Alzheimer’s, tau proteins become abnormally twisted and form tangles inside the cells. These tangles disrupt the normal functioning of brain cells and contribute to the progression of the disease.
### How Do Amyloid Plaques and Tau Tangles Interact?
Research suggests that amyloid plaques and tau tangles work together to cause damage in the brain. Amyloid plaques seem to appear first, often decades before symptoms of Alzheimer’s become apparent. Tau tangles then form in response to the amyloid plaques, leading to further brain damage. This interaction is part of a larger process involving inflammation and cell death, which ultimately results in the cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
### Recent Research and Developments
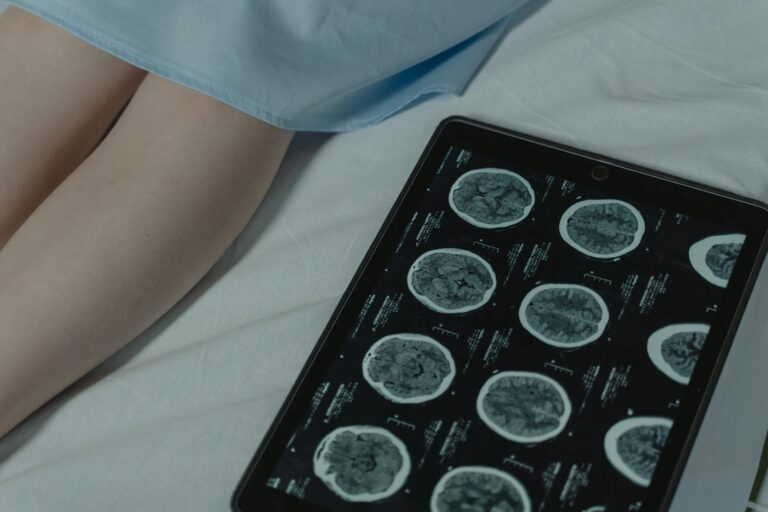
Scientists are actively exploring new ways to diagnose and treat Alzheimer’s disease. For example, researchers are using advanced imaging techniques like MRI to detect changes in the brain associated with amyloid plaques and tau tangles years before symptoms appear. Additionally, studies are investigating how factors like menopause and genetic predispositions influence the development of these protein deposits.
Innovative treatments, such as stem cell therapy, are also being tested to reduce inflammation and prevent further brain damage. These approaches aim to address the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s rather than just its symptoms, offering hope for more effective management of the disease in the future.
In summary, amyloid plaques and tau tangles are key components of Alzheimer’s disease, and understanding their role is essential for developing better treatments. Ongoing research is bringing us closer to early detection and intervention, which could significantly improve outcomes for those affected by this condition.