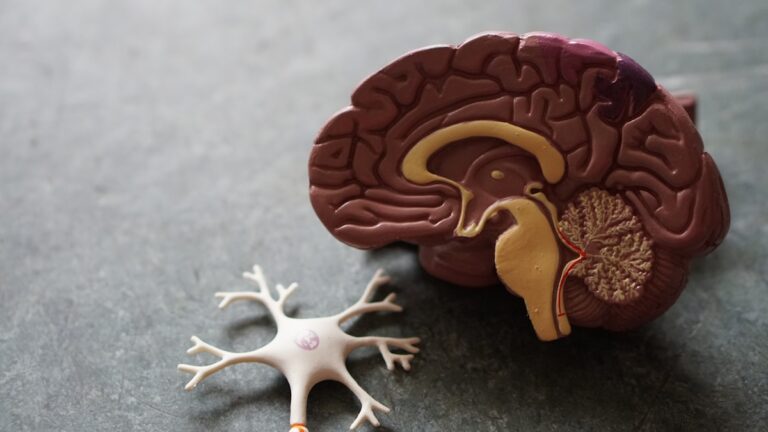
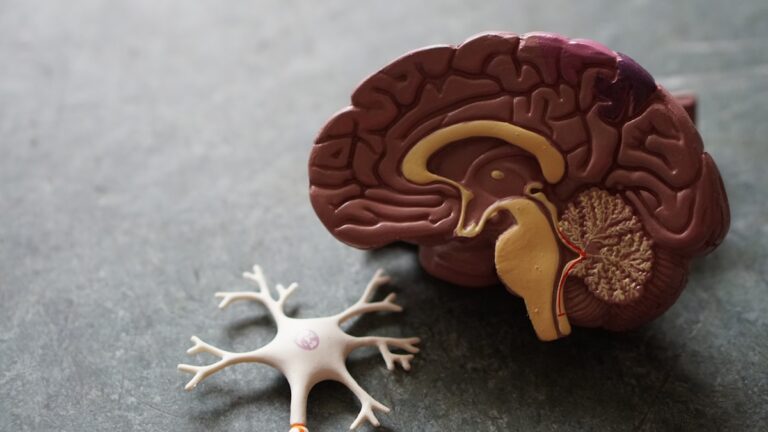
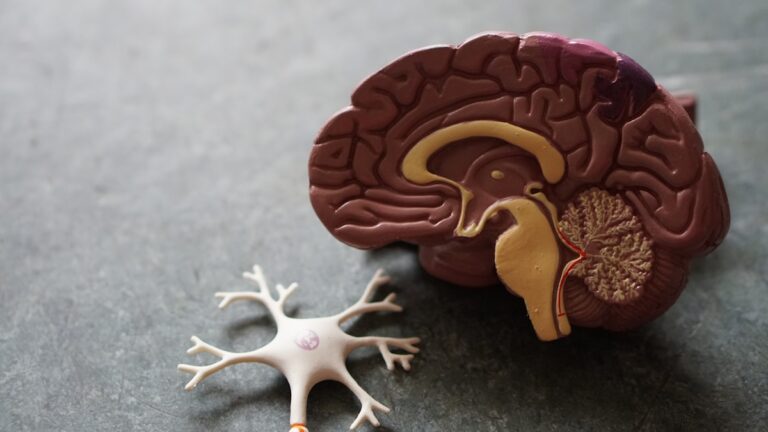
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive and degenerative brain disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is the most common cause of dementia, a term used to describe a decline in cognitive function and memory loss.
The cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still not fully understood, and there is currently no cure. However, researchers have identified certain risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing this disease, and a simple test is now being used to predict an individual’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Before discussing the test, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of Alzheimer’s disease. It is a complex condition that affects the brain in various ways. It is characterized by two types of abnormal structures in the brain – plaques and tangles.
Plaques are clumps of a protein called beta-amyloid that build up between nerve cells in the brain, disrupting communication and causing cell death. Tangles are twisted strands of another protein called tau, which form inside brain cells and disrupt their ability to transport essential nutrients and molecules.
As these plaques and tangles spread throughout the brain, they lead to the death of brain cells, causing a decline in cognitive function and memory loss. This ultimately leads to a person’s inability to perform daily activities and care for themselves.
Identifying Risk Factors
While the exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still unknown, researchers have identified certain risk factors that increase an individual’s chances of developing this condition. These include age, family history, genetics, lifestyle, and certain medical conditions.
Age is the most significant risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. The majority of people with this condition are over the age of 65. As we age, our brain cells naturally degenerate, making us more vulnerable to conditions like Alzheimer’s.
Family history also plays a role in increasing the risk of developing this disease. Those who have a parent or sibling with Alzheimer’s are more likely to develop it themselves.
Genetics also play a role in Alzheimer’s disease. There are two types of genes that can increase the risk of developing this condition – risk genes and deterministic genes. Risk genes increase the likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s, while deterministic genes directly cause the disease.
Lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and chronic stress can also impact the risk of developing this disease. Poor dietary habits, a sedentary lifestyle, and chronic stress can all contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, which has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity, have also been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
The Simple Test for Predicting Alzheimer’s Risk
With an understanding of the risk factors associated with Alzheimer’s disease, researchers have developed a simple test to predict an individual’s likelihood of developing this condition. This test is called the APOE gene test.
APOE is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called apolipoprotein E. This protein helps carry cholesterol and other fats in the bloodstream and plays a role in repairing nerve cells in the brain. However, there are three variations of the APOE gene – APOE e2, e3, and e4.
Studies have shown that the presence of the APOE e4 variant is associated with a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Those who inherit one copy of this variant from one parent have a three-fold higher risk of developing the condition, while those who inherit two copies from both parents have a ten-fold higher risk.
By analyzing an individual’s DNA sample for the presence of the APOE e4 variant, doctors can estimate their risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. If someone has a family history of Alzheimer’s or carries this variant, they may be advised to undergo regular cognitive screenings and take steps to reduce their risk factors.
How Can the Test Help?
The APOE gene test can be used in several ways to help individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Firstly, it can provide peace of mind for those with a family history of the condition. If the test results show they do not carry the APOE e4 variant, they may have a lower risk and can focus on other preventive measures.
Secondly, for those who do carry the APOE e4 variant, early detection can lead to early interventions, such as lifestyle changes and medication, that may slow the progression of the disease or delay its onset. It also allows for more accurate planning of future care needs.
Lastly, the test can also be used in research studies to identify high-risk individuals for potential clinical trials and further our understanding of Alzheimer’s disease.
Final Thoughts
The APOE gene test is a simple and non-invasive way to predict an individual’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. While its accuracy is not 100%, it provides valuable information that can help individuals and their families plan for the future and take necessary steps to reduce their risk.
It is important to remember that a positive result does not mean someone will definitely develop Alzheimer’s disease. It is merely a tool to assess one’s risk and should not be used as a definitive diagnosis. With ongoing research and advancements, we can hope for more accurate and reliable tests in the future to aid in the fight against this devastating disease.