Alzheimer’s disease, also known as Alzheimer tauti, is a progressive and irreversible brain disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It is the most common cause of dementia, which is a term used to describe a decline in cognitive function, including memory, thinking, and behavior. This disease was first described by German psychiatrist and neuropathologist Alois Alzheimer in 1906, and since then, it has been extensively studied and researched.
Understanding Alzheimer’s disease can be complicated and overwhelming, but breaking down the information into simple terms can help us gain a better understanding of this complex disease.
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a type of dementia that gradually destroys brain cells, causing a decline in memory, thinking, and behavior. It is a degenerative and progressive disease, meaning it worsens over time. In the early stages, a person may experience mild memory loss and trouble remembering recent events or names. However, as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more severe, and a person may struggle with daily tasks and even lose the ability to carry on a conversation.
What causes Alzheimer’s disease?
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still unknown. However, scientists believe that a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors may play a role. Studies have shown that family history and genetics can increase the risk of developing this disease. Age is also a significant risk factor – as people age, the risk of developing Alzheimer’s increases. Other factors such as high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes have also been linked to an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
What happens in the brain during Alzheimer’s disease?
The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells that communicate with each other through chemical messages. In Alzheimer’s disease, abnormal deposits of proteins called amyloid plaques and tau tangles develop in the brain. These deposits disrupt the communication between nerve cells, causing them to die. As more and more nerve cells die, the brain shrinks in size, leading to the characteristic symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
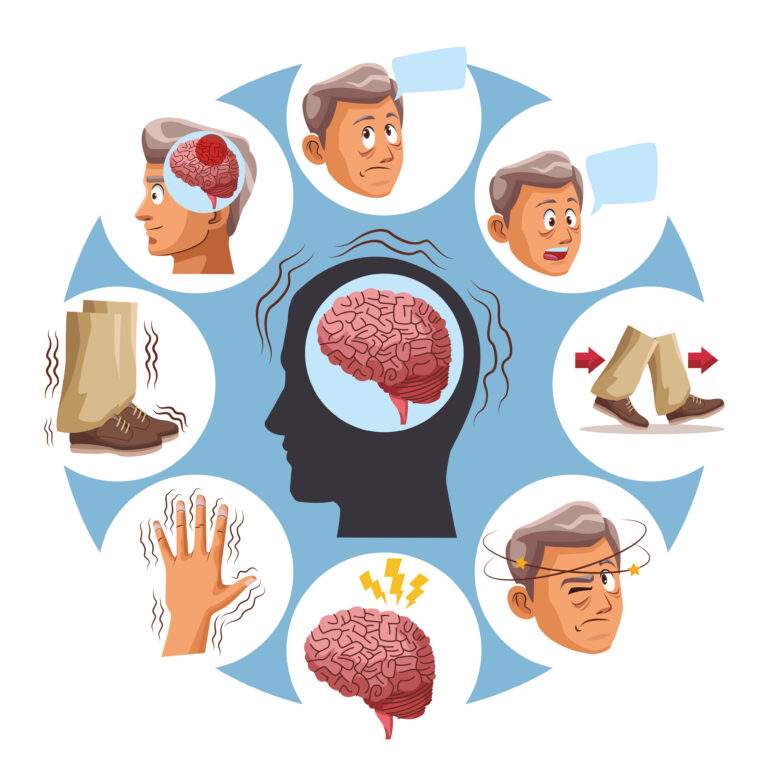
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
The early symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease are often mild and easily overlooked. However, as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more noticeable and can significantly impact a person’s daily life. Some of the common symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease include:
– Memory loss, especially recent events or conversations
– Difficulty performing familiar tasks
– Confusion and disorientation
– Trouble making decisions or solving problems
– Changes in mood and behavior
– Difficulty with language, such as finding the right words or understanding speech
It is essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and a proper diagnosis is necessary to determine if it is Alzheimer’s disease.
How is Alzheimer’s disease diagnosed?
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease can be challenging as there is no single test to confirm it. A thorough evaluation requires a medical history, physical examination, and cognitive tests. The doctor will also conduct blood tests and brain imaging scans to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. A definitive diagnosis can only be made after a post-mortem examination of the brain.
Treatment for Alzheimer’s disease
Unfortunately, there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. However, there are medications available that can help manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. These medications work by enhancing communication between nerve cells or regulating neurotransmitters in the brain. It is crucial to note that these medications may not work for everyone and can only provide temporary relief from symptoms.
Apart from medication, various therapies and techniques can help improve a person’s quality of life with Alzheimer’s disease. These include cognitive training, occupational therapy, and support groups for both the patient and their caregivers.
Caring for someone with Alzheimer’s disease can be physically and emotionally draining, and it is essential to seek support and assistance from healthcare professionals, friends, and family members.
Final thoughts
Alzheimer’s disease is a debilitating and heartbreaking disease that affects not only the person diagnosed but also their loved ones. As the population continues to age, the number of people living with this disease is expected to increase. Therefore, it is crucial to raise awareness and increase research efforts to find effective treatments and, ultimately, a cure for Alzheimer’s disease. In the meantime, we can offer support, understanding, and care for those affected by this disease and their families.